Solutions for those exercises.
Exercises
-
Consider the following tree:
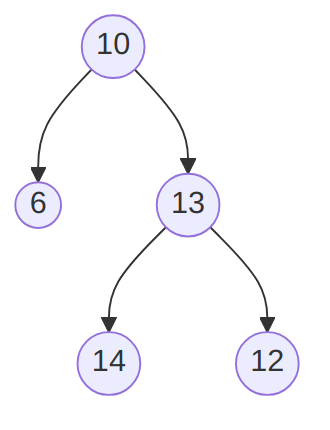
-
Explain why it is not a binary search tree.
-
Pick one among inorder, preorder and postorder traversal, and give
-
A brief description of how it proceeds,
-
What it would produce for the given tree.
-
-
-
Consider the following AVL tree:
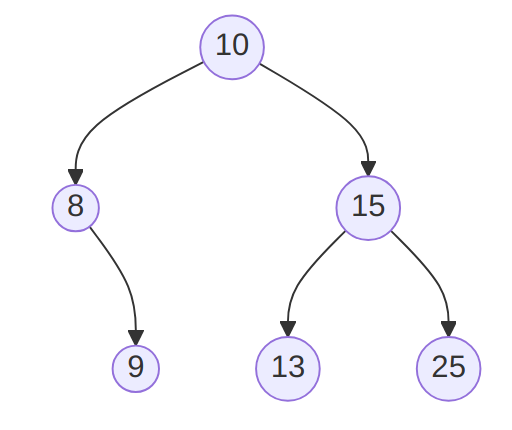
-
Give its inorder traversal.
-
Give an order in which the values could have been inserted (for example, even if this is incorrect, “9, 13, 25, …”) to obtain this tree.
-
Draw next to the drawing the tree obtained after 10 was removed.
-
-
Consider the following implementation of “random” binary trees:
public class RBTree<T> { private class Node { public T Data { get; set; } public Node left; public Node right; public Node( T dataP = default(T), Node leftP = null, Node rightP = null ) { Data = dataP; left = leftP; right = rightP; } } private Node root; public RBTree() { root = null; } public void Insert(T dataP) { root = Insert(dataP, root); } private Node Insert(T dataP, Node nodeP) { if (nodeP == null) { return new Node(dataP, null, null); } else { Random gen = new Random(); if(gen.NextDouble() > 0.5) { nodeP.left = Insert(dataP, nodeP.left); } else { nodeP.right = Insert(dataP, nodeP.right); } } return nodeP; } }Note that the
Insert(T dataP, Node nodeP)method uses thegen.NextDouble() > 0.5test that will be randomlytruehalf of the time, andfalsethe other half.-
Explain the
T dataP = default(T)part of theNodeconstructor. -
Write a
ToStringmethod for theNodeclass, remembering that only a nodeDataneeds to be part of thestringreturned. -
Write a series of statements that would
- create a
RBTreeobject, - insert the values 1, 2, 3, and 4 in it (in this order).
- create a
-
Make a drawing of a possible
RBTreeobtained by executing your code. -
Write a
Findmethod that takes one argumentdataPof typeTand returnstrueifdataPis in theRBtreecalling object,falseotherwise.
-
-
Given the usual implementation of
Node:private class Node { public T Data { get; set; } public Node left; public Node right; public Node(T dataP = default(T), Node leftP = null, Node rightP = null) { Data = dataP; left = leftP; right = rightP; } }Write an
Heightproperty forNode(i.e., a way of computing the longest distance between the callingNodeand a leaf). -
Considering an implementation of binary search trees where
Trealizes theIComparable<T>interface (i.e., where the.CompareTomethod can be used to compare values), write aValueGreaterThanmethod that- takes an argument
dataPof typeT, - returns
trueif there is a value greater than or equal todataPin the binary search tree,falseif there is no value greater thandataPin the binary search tree, or if the tree is empty.
- takes an argument