Another way of implementing lists is to make our class realize the ICollection interface:
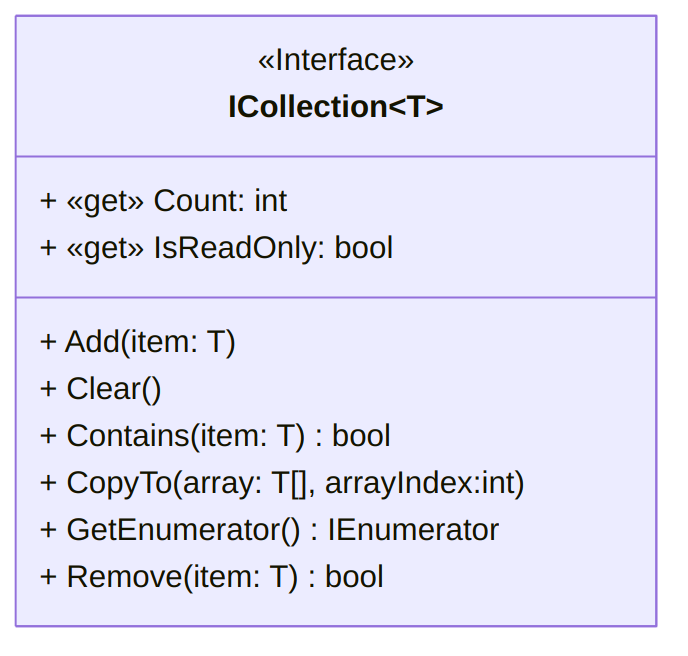
This requires implementing a series of properties and methods:
// Empty
public bool IsEmpty()
{
return first == null;
}
// Add is simply "AddF", slightly revisited.
public void Add(T value)
{
if (isReadonly)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(
"List is read-only."
);
}
first = new Cell(value, first);
}
public void Clear()
{
first = null;
}
public bool Contains(T value)
{
bool found = false;
Cell cCell = first;
while (cCell != null && !found)
{
if (cCell.Data.Equals(value))
{
found = true;
}
cCell = cCell.Next;
}
return found;
}
// Copies the elements of the ICollection to an Array, starting at a particular Array index.
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex)
{
if (array == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(
"The array cannot be null."
);
if (arrayIndex < 0)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(
"The starting array index cannot be negative."
);
if (Count > array.Length - arrayIndex)
throw new ArgumentException(
"The destination array has fewer elements than the collection."
);
Cell cCell = first;
int i = 0; // keeping track of how many elements were copied.
while (cCell != null)
{
array[i + arrayIndex] = cCell.Data;
i++;
cCell = cCell.Next;
}
}
// Remove the first node containing the value
// if it exists and returns true,
// returns false otherwise.
public bool Remove(T value)
{
if (isReadonly)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(
"List is read-only"
);
}
bool removed = false;
if (!IsEmpty())
{
if (first.Data.Equals(value))
{
first = first.Next;
removed = true;
}
else
{
Cell cCell = first;
while (cCell.Next != null && !removed)
{
if (cCell.Next.Data.Equals(value))
{
cCell.Next = cCell.Next.Next;
removed = true;
}
else
{
cCell = cCell.Next;
}
}
}
}
return removed;
}
public int Count
{
get
{
int size = 0;
Cell cCell = first;
while (cCell != null)
{
cCell = cCell.Next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
}
public bool isReadonly = false;
public bool IsReadOnly
{
get { return isReadonly; }
set { isReadonly = value; }
}
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator()
{
Cell cCell = first;
while (cCell != null)
{
yield return cCell.Data;
cCell = cCell.Next;
}
}
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return this.GetEnumerator(); // call the generic version of the method
}