Exercises
-
Consider the following tree:
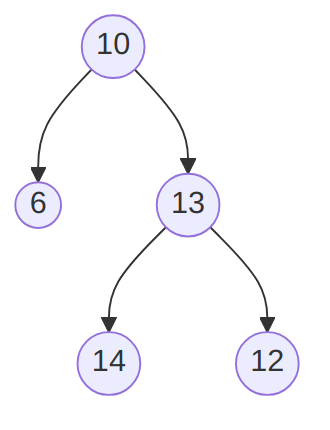
-
Explain why it is not a binary search tree.
Solution
The left child of the node with value 13 has value 14, which is greater than 13, hence violating the binary search tree principle that values in the left sub-tree should be strictly less than the value in the root of the subtree. The same goes for 12.
-
Pick one among inorder, preorder and postorder traversal, and give
-
A brief description of how it proceeds,
Solution
One among the following:
- Inorder traversal processes (recursively) first the left subtree, then the data at the root, then the right subtree.
- Preorder traversal processes (recursively) first the data at the root, then the left subtree, then the right subtree.
- Postorder traversal processes (recursively) first the left subtree, then the right subtree, then the data at the root.
-
What it would produce for the given tree.
Solution
One among the following:
- Inorder gives 6, 10, 14, 13, 12
- Preorder gives 10, 6, 13, 14, 12
- Postorder gives 6, 14, 12, 13, 10
-
-
-
Consider the following AVL tree:
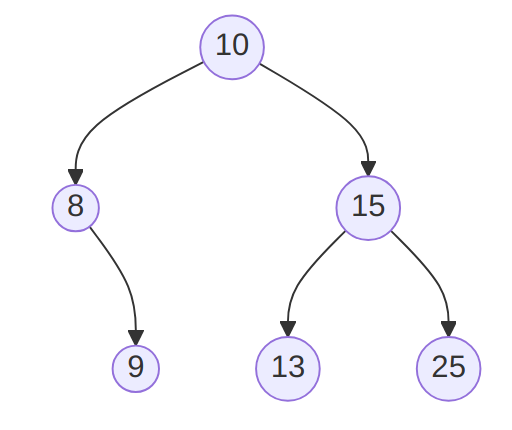
-
Give its inorder traversal.
Solution
8, 9, 10, 13, 15, 25
-
Give an order in which the values could have been inserted (for example, even if this is incorrect, “9, 13, 25, …”) to obtain this tree.
Solution
The values could have been inserted as
- 10, 8, 15, 9, 13, 25
- 10, 15, 8, 9, 13, 25 (permuting 15 and 8),
- 10, 8, 15, 13, 25, 9 (permuting 13, 25, and 9),
or some other variations: the important aspects are:
- Start with 10,
- Do not, while inserting the tree, make it un-balanced (otherwise, the tree would re-balance itself and 10 would not be the root).
If one wants to leverage re-balancing of the tree, then we can use the following sequence:
- 15, 13, 25, 10, 8, 9
Indeed, the tree remains balanced until 9 is inserted: inserting 9 triggers a re-balancing that actually produce the tree given as an example. An example of an incorrect sequence could be
- 15, 13, 8, 9, 25, 10,
as this produces a tree with 13 at its root.
-
Draw next to the drawing the tree obtained after 10 was removed.
Solution
There are two strategies after the root was removed:
- Replacing it with the greatest value on the sub-tree to the left,
- Replacing it with the lowest value on the sub-tree to the right.
The second strategy, which is the one implemented in the lecture notes, gives:
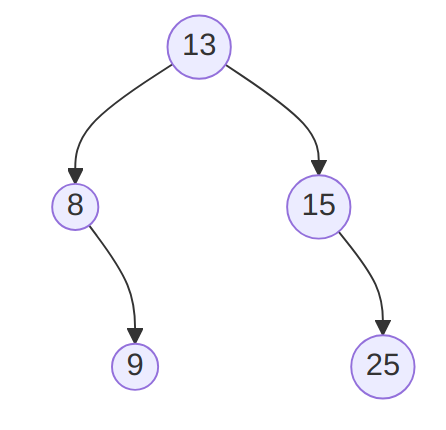
-
-
Consider the following implementation of “random” binary trees:
public class RBTree<T> { private class Node { public T Data { get; set; } public Node left; public Node right; public Node( T dataP = default(T), Node leftP = null, Node rightP = null ) { Data = dataP; left = leftP; right = rightP; } } private Node root; public RBTree() { root = null; } public void Insert(T dataP) { root = Insert(dataP, root); } private Node Insert(T dataP, Node nodeP) { if (nodeP == null) { return new Node(dataP, null, null); } else { Random gen = new Random(); if(gen.NextDouble() > 0.5) { nodeP.left = Insert(dataP, nodeP.left); } else { nodeP.right = Insert(dataP, nodeP.right); } } return nodeP; } }Note that the
Insert(T dataP, Node nodeP)method uses thegen.NextDouble() > 0.5test that will be randomlytruehalf of the time, andfalsethe other half.-
Explain the
T dataP = default(T)part of theNodeconstructor.Solution
This makes the first argument of the constructor optional: if no value is provided, then the default value for
Tis used. For example, forint, then 0 would be used. -
Write a
ToStringmethod for theNodeclass, remembering that only a nodeDataneeds to be part of thestringreturned.Solution
public override string ToString() { return Data.ToString(); } -
Write a series of statements that would
-
create a
RBTreeobject, -
insert the values 1, 2, 3, and 4 in it (in this order).
Solution
RBTree<int> btree = new RBTree<int>(); btree.Insert(1); btree.Insert(2); btree.Insert(3); btree.Insert(4);
-
-
Make a drawing of a possible
RBTreeobtained by executing your code.Solution
Any binary tree containing 1, 2, 3 and 4, with 1 at the root, 2 a child of 1, 3 a child of 1 or 2, and 4 a child of 1, 2 or 3, is correct. One such example is:
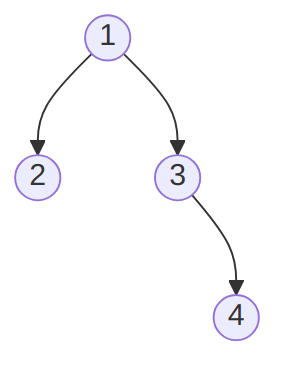
-
Write a
Findmethod that takes one argumentdataPof typeTand returnstrueifdataPis in theRBtreecalling object,falseotherwise.Solution
public bool Find(T dataP) { bool found = false; if (root != null) { found = Find(root, dataP); } return found; } private bool Find(Node nodeP, T dataP) { bool found = false; if (nodeP != null) { if (nodeP.Data.Equals(dataP)) { found = true; } else { found = Find(nodeP.left, dataP) || Find(nodeP.right, dataP); } } return found; }
-
-
Given the usual implementation of
Node:private class Node { public T Data { get; set; } public Node left; public Node right; public Node(T dataP = default(T), Node leftP = null, Node rightP = null) { Data = dataP; left = leftP; right = rightP; } }Write an
Heightproperty forNode(i.e., a way of computing the longest distance between the callingNodeand a leaf).Solution
The one provided in the lecture notes is:
public int Height { get { int height = 0; if (left != null && right != null) { height = Math.Max(left.Height, right.Height) + 1; } else if (left != null) { height = left.Height + 1; } else if (right != null) { height = right.Height + 1; } // The last case is if both children // are null, in which case the height // remains 0. return height; } } -
Considering an implementation of binary search trees where
Trealizes theIComparable<T>interface (i.e., where the.CompareTomethod can be used to compare values), write aValueGreaterThanmethod that- takes an argument
dataPof typeT, - returns
trueif there is a value greater than or equal todataPin the binary search tree,falseif there is no value greater thandataPin the binary search tree, or if the tree is empty.
Solution
The one provided in the lecture notes is:
public bool ValueGreaterThan(T dataP) { bool returned = false; if (root != null) { returned = ValueGreaterThan(dataP, root); } return returned; } private bool ValueGreaterThan(T dataP, Node nodeP) { bool returned = false; if (nodeP != null) { if (dataP.CompareTo(nodeP.Data) > 0) // dataP > nodeP.Data return ValueGreaterThan(dataP, nodeP.right); // We only need to go right, since values will decrease // if we go left. else returned = true; } return returned; } - takes an argument