General Rules
Attributes and Properties
| Type of Attribute or Property | |
|---|---|
| Public attribute | + attribute : [data type] |
| Private attribute | - attribute : [data type] |
| Public property | + «property» Property : [data type] |
| Private property | - «property» Property : [data type] |
Methods with Return Type
| Type of Method | |
|---|---|
| Public method with no arguments | + Method() : [return type] |
| Private method with no arguments | - Method() : [return type] |
| Public method with arguments | + Method(argument1 : [data type 1], …, argumentn : [data type n]) : [return type] |
| Private method with arguments | - Method(argument1 : [data type 1], …, argumentn : [data type n]) : [return type] |
Methods with Void or No Return Type
| Type of Method | |
|---|---|
| Public method with arguments | + Method(argument1 : [data type 1],…, argumentn : [data type n]) |
| Private method with arguments | - Method(argument1 : [data type 1],…, argumentn : [data type n]) |
Special Cases
| Case | How to Change UML Formatting |
|---|---|
| Static | Underline |
| Abstract | Italicize |
| Protected | # instead of + or - |
| Abstract class | Add «Abstract» above class name |
| Interface | Add «Interface» above class name |
Relationships (Arrows)
| Arrow Type | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Open arrow with solid line (⇽) | Inheritance |
| Open arrow with dashed line (◁┈) | Realization |
Examples
Simple Example
For example, in the following UML class diagram:
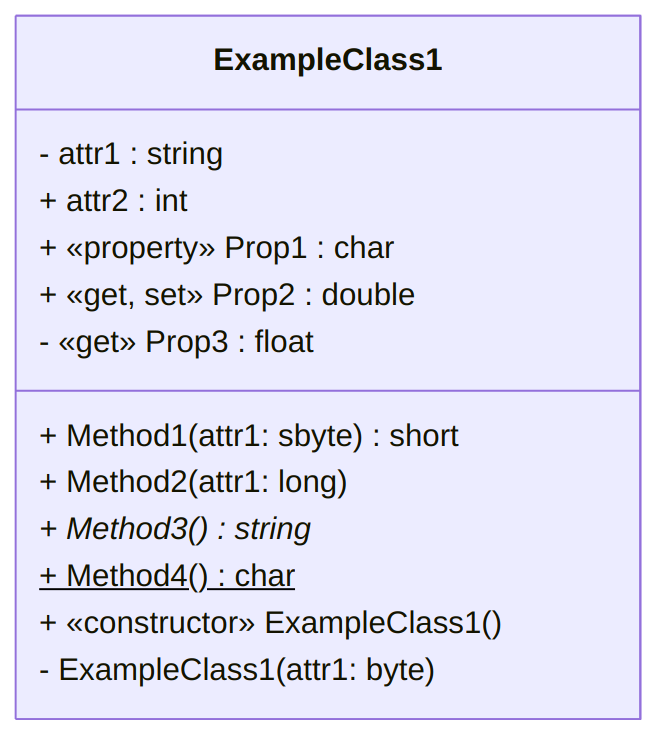
Attributes
attr1isprivateand of typestring,attr2ispublicand of typeint,
Properties
Prop1is apublicproperty of typechar(that may have both asetand aget, or only one of them),Prop2is apublicproperty of typedoublethat must contain both asetand aget,Prop3is aprivateproperty of typefloatthat contains only agetand noset,
Methods
Method1is apublicmethod that takes as an argument asbyteand returns ashort,Method2is apublicmethod that takes as an argument alongand does not return anything (that is, its return type isvoid, here omitted),Method3is apublicabstract method that does not take any argument and returns astring,Method4is apublicstatic method that does not take any argument and returns achar.
Constructors
- The first
ExampleClass1is apublicconstructor that does not take any argument (and does not have any return type), - The second
ExampleClass1is aprivateconstructor (we know it even if the indication «constructor» is missing, since it has the same name as the class) that takes as an argument abype(and does not have any return type)
Forbidden Combination
Note that the following does not make sense:
- A static method cannot be abstract,
- An attribute cannot be abstract,